For business leaders looking to drive digital and business transformation, go FullStride.
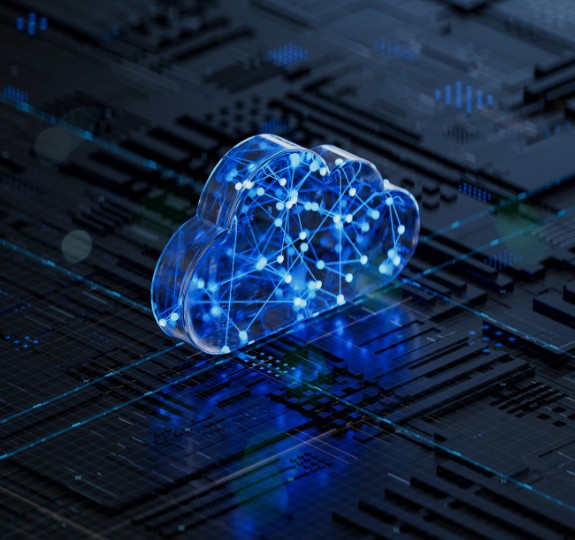
Today’s CXO conversation is focused on delivering transformational business outcomes in the cloud. And Wipro FullStride Cloud's deep engineering and infrastructure experience uniquely positions Wipro as a strategic partner of choice.
For ecosystem orchestration that drives next-level experiences and innovation, go FullStride.
For operational efficiency and sustainability, go FullStride.
To unlock data insights with AI and ML to create full-stack, cloud-native enterprises, go FullStride.
To truly thrive in the cloud, go FullStride.
 Locations
Locations