Artificial Intelligence (AI) has from the very beginning of the pandemic been busily working behind the scenes assisting the limitations of human knowledge in the massive endeavor of understanding and tracking the spread of COVID-19. Today multiple AI-powered projects based on data science, machine learning, and big data are being used across a broad range of fields to predict, explain, and manage the different scenarios caused by the health crisis. With AI use growing in the healthcare sector, it’s predicting early COVID-19 symptoms and thereby control the spread of the infection. It’s also being used to screen and track patients, as well as predict future infections, using algorithms that process data to identify insightful patterns.
Machine learning is the main driving force behind AI’s capability to detect these patterns. For example, in a given country, it may be possible to predict the number of deaths from COVID-19 in males over 60.
This technology’s algorithms allow healthcare organizations to effectively diagnose and customize medical care and follow-up plans, resulting in better patient experiences. AI is helping drive COVID-19 prevention at the molecular level (e.g., drug and vaccine discovery), the patient level (e.g., patient diagnosis), and the population level (e.g., epidemiological surveillance). As the following images outlines, AI enables physicians to accelerate their ability to treat patients and deliver effective care.
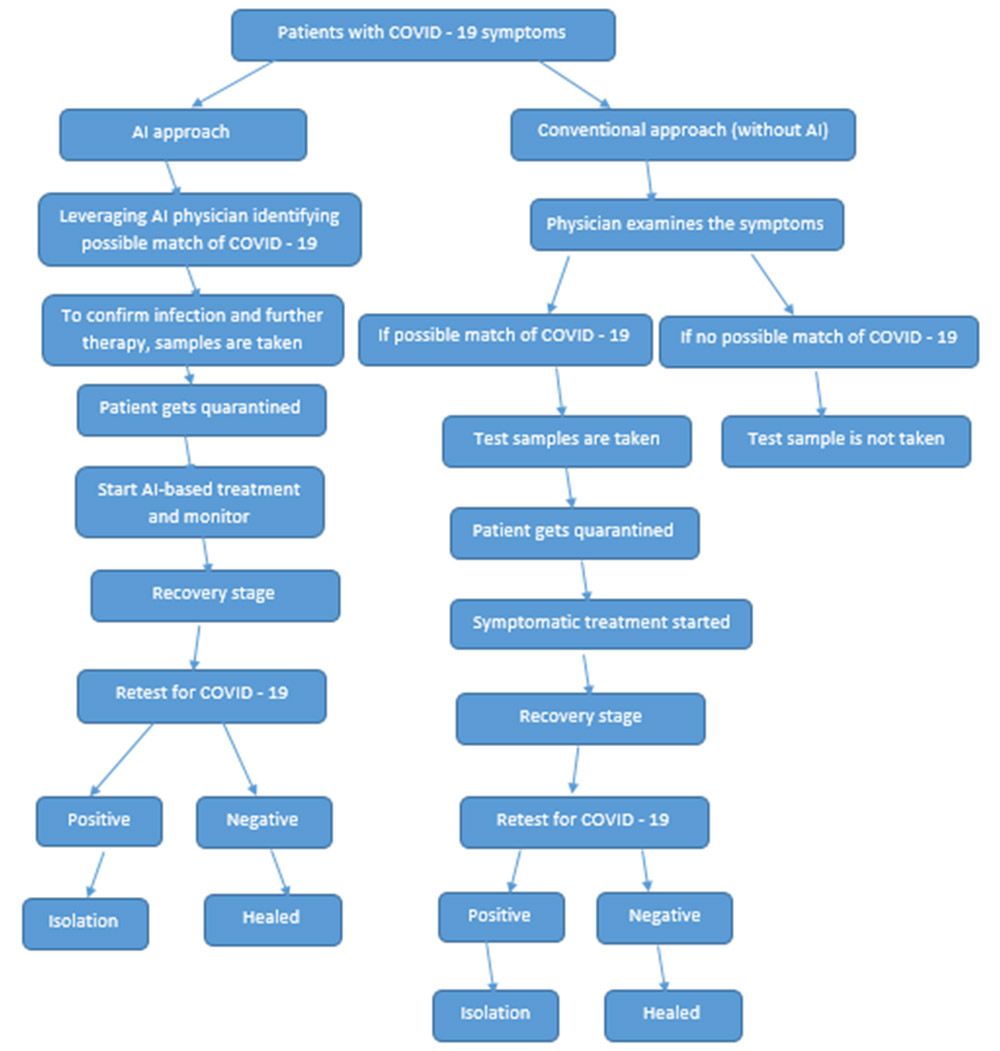
Prediction and Tracking
Healthcare professionals are studying the transmission rate of the pandemic by using AI in conjunction with these mathematical models:
These models can theoretically predict the number of positive cases and the rate of transmission. Once these models have produced data, researchers can upload that data into HealthMap, an online information resource that collects the publicly available COVID-19 data, making it readily available to facilitate the effective tracking of its spread.
Recently, AI has helped identify and forecast COVID-19 outbreaks by employing multidimensional data. Regularly, AI-driven tools are limited to one data type, which may not lead to an accurate measurement of the coronavirus’s spread. In such a case, the use of multidimensional data can help support decision-making processes with higher reliability.
As an example, AI is being used with anomaly detection (AD), which identifies abnormal and unfamiliar patterns in a medical image (such as a chest X-ray). AD can also be applied to either single-dimensional or multidimensional data. Without AI, AD-driven processes would be tedious for physicians to analyze and provide treatment for patients. Using the data AD generates, AI can be used to identify the most vulnerable regions by tracking the number of confirmed cases and recommending the necessary actions to curtail the spread.
AI-based Vaccine Discoveries and Predictions
Since the outbreak of the coronavirus, several AI-based approaches have been used to design vaccines. Natural language-processing models, especially language-modeling techniques, have helped drive COVID-19 vaccine discovery. These models’ algorithms analyze the data, which includes geographic locations and patients’ social interactions, and provides recommended treatments, facilitating vaccine development. AI is also being used with the Vaxign machine-learning platform, which is based on supervised classification models, to accelerate the discovery process.
AI is also furthering COVID-19 research in three major areas: binary diagnosis (whether COVID-19 is present or absent), studying lung abnormalities, and distinguishing COVID-19 from non-COVID-19 pneumonias. AI tools can predict the patient’s need for oxygen therapy or incubation and the development of acute respiratory distress syndrome. With AI platforms, healthcare teams can determine the generalizability of treatments to multinational patient populations, integrate imaging and clinical information, analyze serial imaging data, and customize patients’ steroid treatments. Additionally, by using natural-language tools to process clinical reports, machine-learning models are assessing radiology images to predict the need for intensive care unit admissions.
Wipro’s AI Solutions for Detecting COVID-19
Wipro is contributing to pandemic efforts and has developed a fully automated AI tool that detects COVID-19 based on CT scan images or chest X-rays. Our research teams have also developed the Covigilent app in association with Healthcare Global Enterprises (HCG) supported by the Karnataka government, Bhakti Vedanta Hospital in Mumbai, and Bangalore Medical College and Research Institute (BMRCI).
Using deep-learning and machine-learning algorithms, the app is an advanced AI-powered cough-analysis and rapid COVID-19–screening tool. It helps in premature detection efforts, with a person’s cough being the primary metric. The app discriminates COVID-19 coughs from those due to seasonal bronchitis and pneumonia. It captures audio and data, such as gender, age, and other health points, which are uploaded to a secure cloud server. AI algorithms then analyze the audio signals and identify those who are infected.
Healthcare organizations are in crucial need of real-time decision-making technologies to help them decrease the spread of the coronavirus. AI’s ability to mimic human intelligence in a proficient way is enabling healthcare professionals to quickly to understand the nature of the virus and develop vaccines for reducing its spread. This results-driven technology is driving screening efforts, analysis, predictions, and the tracking of current and likely future patients. It’s also playing a role in tracking the confirmed, recovered, and fatality cases, enabling physicians to gain important insights on how to treat patients and end the pandemic.

Radha Vuppalapati
Lead Consultant Data Analytics & AI, Wipro
Radha is an expert in multiple analytical tools, data-mining methodologies, and cloud computing technologies. She has worked on various analytics projects in the energy and utilities and banking domains. Her experience includes data analysis, proposing analytical solutions, generating dynamic reports, and other data preparation components, such as data pre-processing, profiling, cleansing, validation, and transformation.