What is Services-as Software (SaS)?
If SaaS (Software as a Service) gives you a calculator, Services-as Software (SaS) delivers the accountant. This distinction captures the shift happening in enterprise technology today. SaS describes solutions that don't just assist people—they perform end-to-end services through autonomous AI agents, under light supervision. While Software as a Service offers tools that augment human productivity, Services-as Software platforms use agentic AI to handle job functions previously carried out by knowledge workers. In essence, customers pay for results—a resolved ticket, a reviewed contract, a matched invoice—not for platform access or seats. This transforms labor into a scalable product, aligning prices with outcomes.
SaS differs from traditional models in three fundamental ways:
Automated Outcomes: The software is the worker, replacing tool-centric workflows.
Agentic AI at the Core: SaS solutions built on AI architectures can make decisions, reason through ambiguity, learn and adapt in real-time, and execute multi-step workflows.
Outcome-Linked Economics: Pricing shifts from subscription models to usage, transaction or outcome-based models directly aligning vendor incentives to customer success.
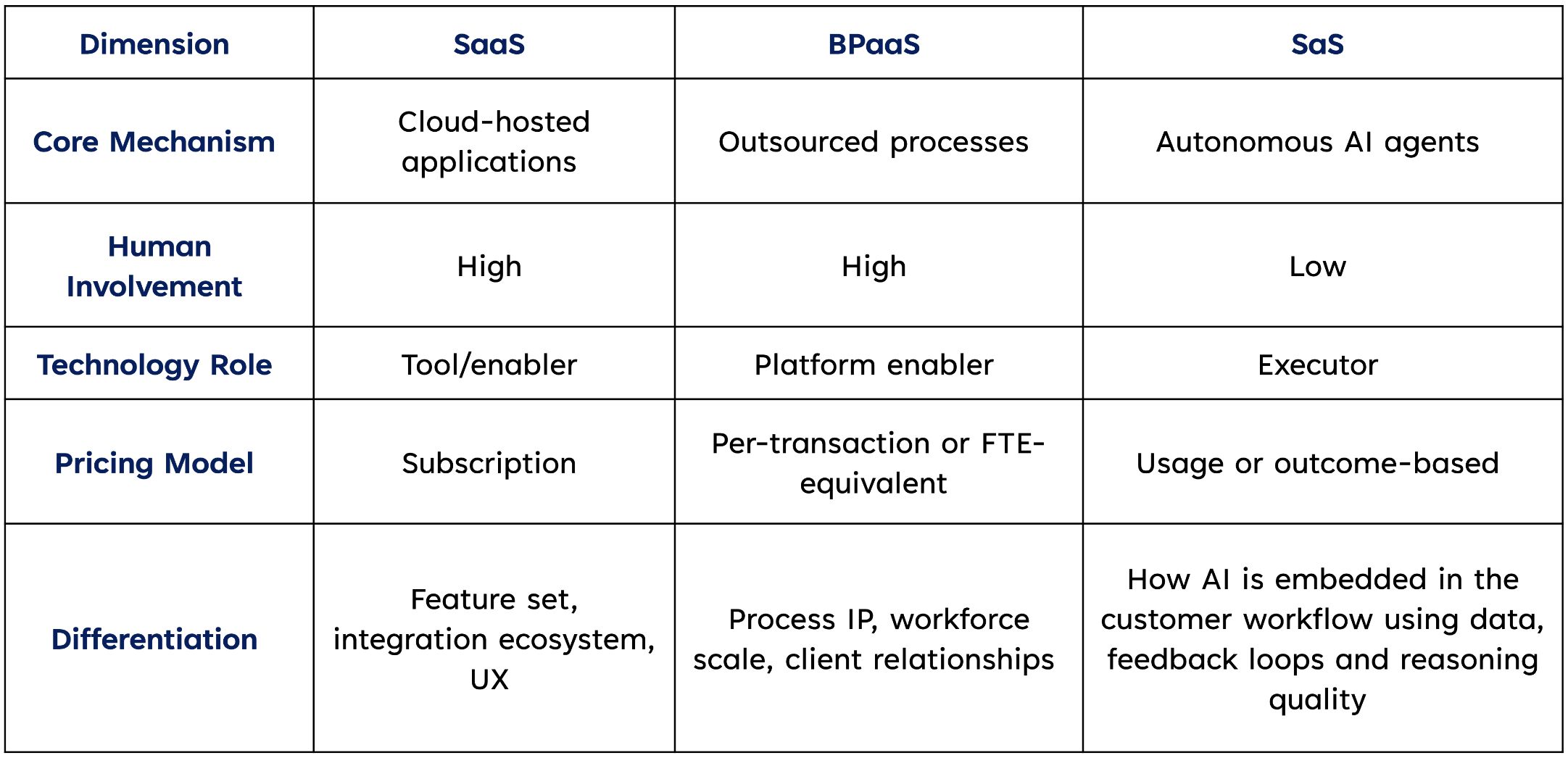
SaaS vs. BPaaS vs. SaS—What Actually Changes?
Business Process as a Service (BPaaS) showed that technology platforms plus human operations could deliver outcome-based services. SaS keeps the outcome promise but makes AI agents the executor.
Here's what changes: