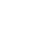Quantum Computing is set to redefine Biomedical Innovation
Biomedical research is entering a transformative era, driven by the convergence of life sciences and quantum computing. As the biotech industry faces unprecedented data volumes and increasingly complex molecular challenges, quantum computing offers a new way forward. It can address problems that classical computers struggle with, such as simulating molecular interactions at atomic precision, analysing massive genomic datasets, and optimising clinical trials.
From accelerating drug discovery to supporting personalised medicine, quantum technology is beginning to reshape what is possible in biomedical research. With many leading pharmaceutical companies already exploring quantum applications, early adopters stand to gain a decisive competitive advantage as this next frontier of healthcare innovation evolves.
Addressing Biomedicine’s Toughest Challenges with Quantum
Despite remarkable progress in computational biology, classical computing continues to face limitations that hinder innovation across biomedical R&D. Quantum computing directly addresses several of these pain points.
Complex Molecular Simulations
Drug discovery depends on understanding molecular behaviour: how proteins fold, how drugs bind to targets, and how reactions occur at the atomic level. Classical computers approximate these interactions but struggle with accuracy beyond small molecules, as quantum mechanical complexity scales exponentially. Quantum computers, operating on quantum principles, can simulate molecular systems with far greater fidelity. This capability could dramatically reduce the time and cost of drug discovery by enabling more accurate predictions of molecular properties.
Exploding Data in Genomics and Imaging
Biomedical data, from genome sequencing to MRI scans, is growing faster than classical algorithms can efficiently process. Identifying subtle disease biomarkers or enhancing medical images from limited samples requires considerable computational power. Quantum algorithms can explore high-dimensional data spaces more efficiently, uncovering patterns like rare genetic variants or subtle imaging features that classical analytics may miss. This could support faster diagnostics and more precise treatment planning.
Optimizing Clinical Trials
Designing clinical trials involves optimising patient cohorts, dosages, and protocols across numerous possible combinations. Classical statistical methods often yield suboptimal designs. Quantum computing’s ability to evaluate many combinations simultaneously could improve trial efficiency, reduce costs, and accelerate timelines to approved therapies.
The Emerging Quantum Advantage in Biomedical Research
Although quantum computing is still in its nascent stages, hybrid quantum–classical approaches are demonstrating promising results in biomedical research.
Accelerating Small-Molecule Simulation
Quantum computers can simulate the quantum chemistry of small molecules with impressive accuracy. Using algorithms like the Variational Quantum Eigensolver, researchers have simulated molecules like hydroxyl cation (OH+) on current quantum hardware. At Wipro’s Innovation Labs, experimental demonstrations showed that quantum computation achieves 2.3× higher accuracy and 10× faster performance than classical methods under controlled conditions. These results validate that quantum methods can complement and outperform classical simulations in both speed and precision, even on today’s limited devices.
Improving Genomic Data Analysis
Quantum algorithms are being explored to accelerate DNA sequence alignment and mutation detection. By encoding genomic data into quantum representations, researchers have reported faster alignment and variant identification in experimental settings compared to classical bioinformatics tools. This capability could shorten timelines for analysing patient genomes and enable quicker insights into disease risk and treatment response.
Detecting Diseases Earlier with Quantum Machine Learning (QML)
QML models are showing promise in identifying disease biomarkers and classifying complex biological patterns. A study on quantum cancer classification demonstrated that quantum neural networks can effectively classify multiple cancer types from thousands of gene expression profiles, outperforming classical models in accuracy. Quantum approaches can be particularly effective at detecting subtle patterns in noisy or small datasets, supporting earlier disease detection and discovery of new therapeutic targets.
Medical Imaging Enhancement
Quantum-enhanced imaging algorithms and quantum-inspired techniques have exhibited significant improvements in image clarity and processing efficiency in experimental environments. A 2025 quantum‑enhanced imaging prototype study has reported more than 30% sharper MRI reconstructions and up to 60% lower radiation doses for CT imaging, while maintaining diagnostic quality and improving patient safety. These advances highlight quantum computing’s potential to revolutionise medical imaging and diagnostics.
Preparing for the Quantum‑Powered Future of Biomedical R&D
Quantum computing is expected to evolve from proof-of-concept experiments to integrated tools within biomedical workflows, as hardware continues to scale (from tens to hundreds of high-quality qubits).
Quantum Protein Folding and Drug Design – Expected Breakthrough in Next 2–3 Years
Quantum processors with ~100 stable qubits may begin addressing medium-sized protein folding problems and more complex molecular dynamics. This could enable more accurate simulations of protein structures associated with diseases like Alzheimer’s and support drug binding studies with greater precision. Quantum-enhanced simulations are expected to complement classical molecular dynamics, shortening drug discovery cycles and reducing reliance on trial-and-error experimentation.
Quantum‑Accelerated Clinical Trial Design Within Five Years
Quantum algorithms could assist in designing smarter clinical trials by rapidly evaluating up to millions of patient stratification schemes and dosing regimens. For example, quantum algorithms may help identify optimal cohort compositions by factoring genetic markers and demographics variables, leading to shorter trials, improved success rates, and faster progression toward regulatory approval.
Quantum‑Native Diagnostics in the Next Decade
Hospitals and research centres could increasingly adopt quantum-enhanced imaging diagnostics. Quantum sensors could provide ultra-sensitive measurements for more precise diagnostics. QML could enable ultra-fast image reconstruction and anomaly detection, allowing radiologists to identify subtle tumour boundaries or abnormalities instantly.
Longer term, quantum AI systems may support continuous analysis of patient data streams to predict health issues and inform treatments—acting as a quantum decision-support “co-pilot” for clinicians.
A Practical Roadmap to Quantum Readiness for Pharma and Biotech
For pharmaceutical and biotech companies, the question is no longer if quantum computing will impact industry, but how soon and how best to prepare. At Wipro, we recommend a phased approach to building quantum readiness.