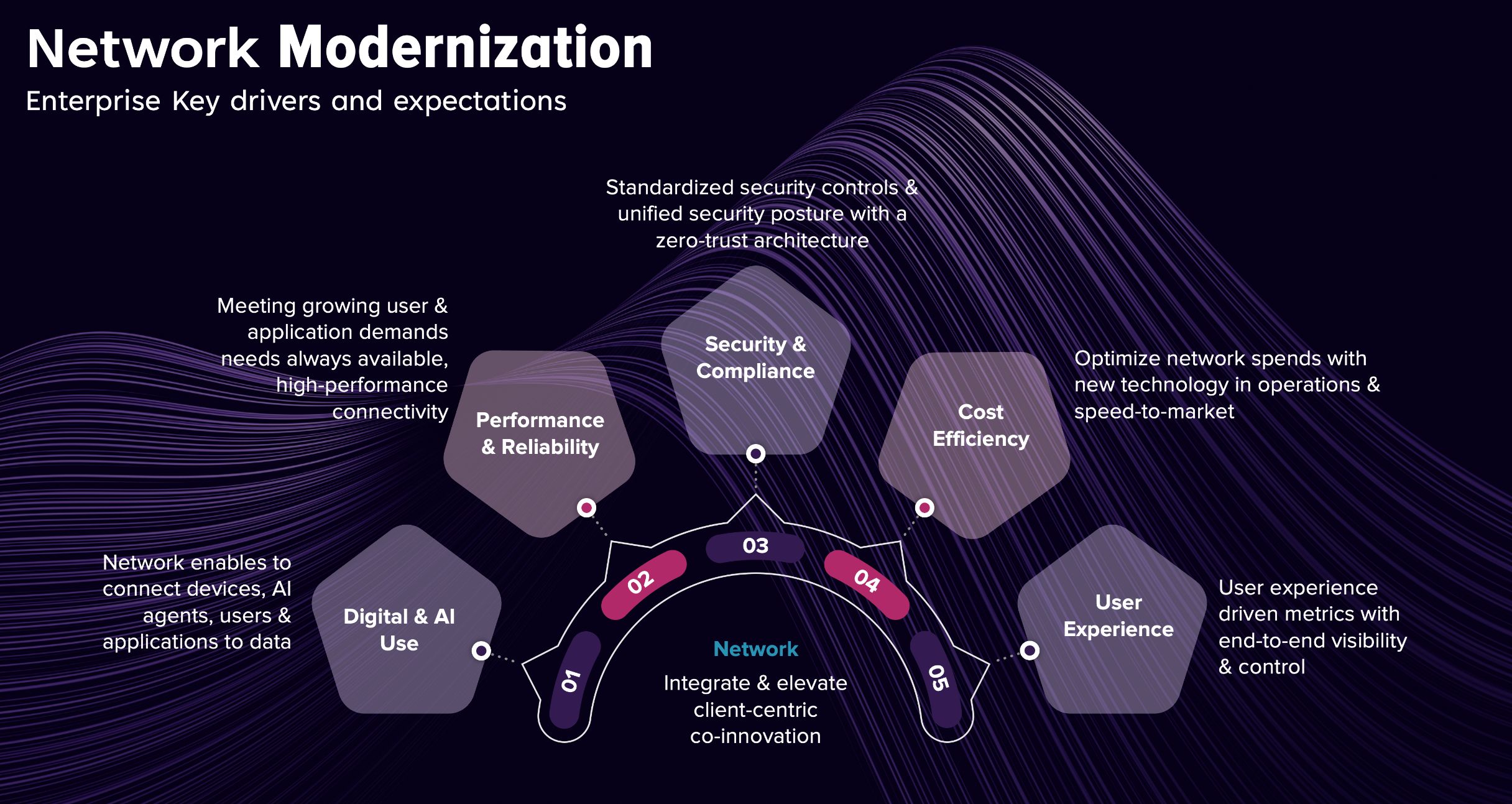
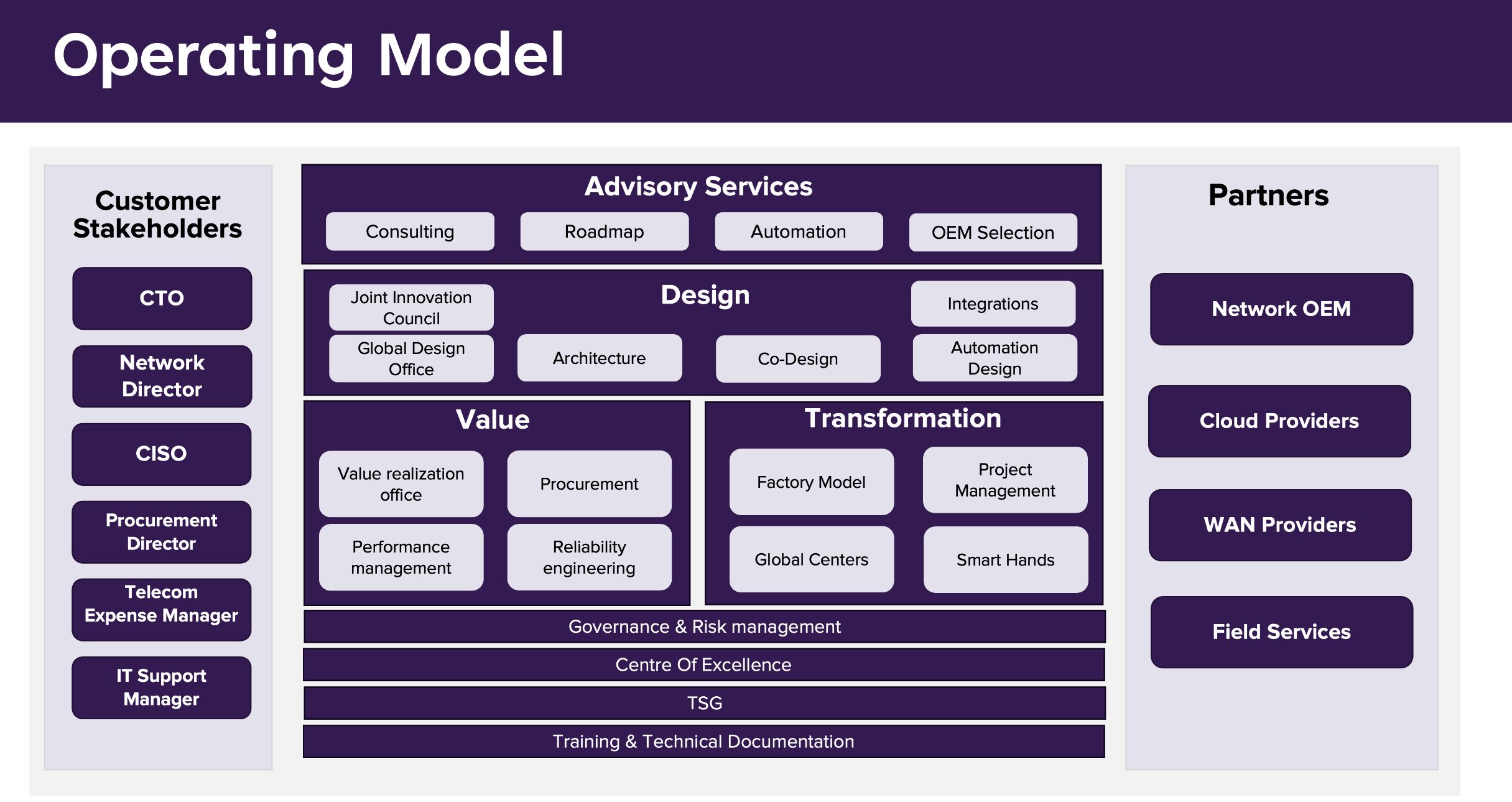
What is Network Modernization?
In an era marked by a global workforce operating on both cloud and on-premises workloads, achieving business goals demands a modernized and future-proof network. Enterprise network modernization needs to be viewed holistically, as focusing on only a few components of the network may lead to increased costs and unnecessary business disruptions. A modernized network signifies an end-to-end network transformation that is flexible, cost-effective, and AI-driven.
Why Network Modernization?
With the advent of the cloud, hybrid workload infrastructure has become common across enterprises, and users now require flexible access to enterprise workloads regardless of their location.
Investments in the network domain have lagged behind advancements in compute, storage, and cloud infrastructure. However, with the rise of software defined networking (SDN) and AI for networks, the network domain has become a foundational investment.
Enterprises face market-driven challenges and opportunities that necessitate network modernization.
Some recent examples of challenges witnessed across industries include:
- A multinational bank faced urgent regulatory risks and required the rapid replacement of 80% of its 20,000 aging wireless access points within a year.
- A global manufacturing company with centralized data centres and a traditional WAN experienced slow transactions due to high latency, performance bottlenecks, and security compliance challenges.
- A UK energy company struggled with a non-standard, unmanaged legacy network, resulting in poor performance, audit non-compliance, and management challenges.
- A global FMCG company operated a highly distributed LAN infrastructure characterized by inconsistent standards and limited hardware resources, which led to delays in time-to-market, management challenges, reduced performance, and increased operational costs.
1. Security
- Vulnerabilities in legacy devices due to limited security controls.
- Lack of OEM support on legacy devices due to end-of-life (EOL)/ end-of-support (EOS) status.
- Absence of a unified security posture for hybrid user access and multi-platform applicationsss
2. Unplanned spending
- Ad hoc spending on short-term projects leading to a siloed approach
- Lack of a holistic network modernization strategy
- Future projects potentially rendering past transformations obsolete, leading to extra spending
3. Fragmented roadmaps
- Rework and project failures due to changing roadmap
- Lack of long-term transformation plans with a narrowed focus on short-term successes
- The need for prioritized and structured roadmap for short-, mid- and long-term transformation goals
4. User Experience
- Inferior performance due to non-optimal traffic paths
- Impact on adoption of new services such as cloud and internet
- Lack of visibility or control over user experience metrics
- Minimal automation leading to higher issue resolution times
5. Velocity
- Time-consuming transformations leading to project overruns
- Unpredictable results and delays due to non-standardized processes