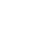Financial Crime Escalates as Legacy Systems Fall Behind
The financial services industry is facing an inflection point in its battle against fraud and money laundering. As digital transactions accelerate and criminal tactics become more sophisticated, traditional detection systems—often rule-based and siloed—are struggling to keep pace. According to the Association of Certified Fraud Examiners (ACFE), financial institutions lose an estimated 5% of their annual revenue to fraud. Meanwhile, global Anti-Money Laundering (AML) fines exceeded $5 billion in 2023 alone, highlighting the regulatory and reputational risks faced by banks.
Several systemic issues within the banking infrastructure contribute to this challenge. Many institutions still depend on legacy systems that lack real-time detection capabilities, making them slow to respond to emerging threats. Data silos across departments limit visibility into customer behavior and transaction patterns, hindering comprehensive risk assessment. Manual processes further delay response times and inflate operational costs.
AI is no longer just a tool—it’s becoming the backbone of modern fraud and AML strategies. By enabling real-time monitoring, adaptive learning, and intelligent automation, AI empowers financial institutions to move from reactive compliance to proactive risk management.
AI as a Game-Changer in Fraud Detection
Many solutions are emerging in the field of fraud detection, primarily leveraging machine learning (ML) algorithms that analyze vast amounts of transaction data to identify suspicious activities in real time. This enables banks to prevent fraud before it occurs, protecting both the institution and its customers, while ensuring the security of payment flows.
Here is the process of detecting and preventing fraudulent activities in payment systems:
- Pattern Recognition
AI algorithms analyze transaction data to identify patterns and anomalies that may indicate fraudulent behavior. For example, sudden large transactions or unusual spending patterns can trigger alerts. - Real-Time Monitoring
AI systems monitor transactions in real time, enabling immediate detection and response to suspicious activities. This proactive approach helps prevent fraud before it causes harm. By combining geo-spatial information, AI systems become more accurate and comprehensive. For example, they can detect anomalies such as significant geographical distances between simultaneous purchases or mismatches between a customer's physical location and the transaction initiation point. - Behavioral Analysis
AI analyzes customer behavior & spending patterns to detect deviations from typical purchasing trends. For instance, a drastic change in a customer’s spending habits may signal potential fraud. - Machine Learning Models
AI employs machine learning models that continuously learn and adapt to new fraud tactics. These models can predict and identify fraudulent activity based on historical data and emerging trends.
For example, PayPal uses AI to monitor transactions in real time, triggering additional verification steps when anomalies are detected—such as unusual device usage or location changes. Mastercard leverages AI to analyze global transaction patterns, enabling proactive fraud prevention across its network.
AI as a Strategic Enabler for AML
AI helps fight money laundering by spotting unusual patterns and flagging suspicious transactions. Automating these checks allows banks to follow rules more easily and lowers the chance of financial crime.
The key use cases include:
- Transaction Monitoring
AI systems monitor transactions for indicators of money laundering, such as large transfers, frequent transactions, or dealings with high-risk countries. - Customer Risk Profiling
AI can generate risk profiles for customers based on their transaction history, behavior, and other relevant factors. This helps in identifying high-risk individuals and entities. - Entity Resolution
AI can resolve entities involved in transactions by identifying connections between different accounts and individuals, which may suggest money laundering activities. - Automated Reporting
AI can automate the creation of Suspicious Activity Reports (SARs), ensuring timely and accurate reporting to regulatory authorities.
For example, HSBC uses AI to detect suspicious patterns and automate SAR filings, improving compliance efficiency. Standard Chartered uses AI to monitor transactions, detect potential money laundering, build customer risk profiles, and automate reporting.
Strategic Roadmap for Implementing AI
Implementing AI for fraud detection and anti-money laundering (AML) is a high-impact initiative that demands a structured strategy. The following roadmap offers clear, actionable steps banks can take to deploy AI effectively and drive long-term value.
- Regulatory Compliance
AI implementations must align with all applicable regulatory requirements, including compliance with data privacy laws, AML directives, and fraud reporting standards. Systems should be auditable, transparent, and capable of generating accurate regulatory reports. This is an ongoing consideration that must be integrated from the very beginning, even before the model development starts. - Data Integration
Banks must integrate AI systems with their existing data infrastructure to ensure seamless access to transaction records, customer profiles, and other relevant data. A unified data environment is essential for training accurate models and facilitating real-time decision-making. However, data integration is only one part of the process— cleaning the data and ensuring its reliability and quality are even more critical. - Training and Development
To maximize the value of AI, banks need to invest in upskilling their workforce. This includes training staff to understand how AI systems function, interpret AI-generated insights, and apply them effectively in fraud detection and AML operations. - Continuous Improvement
AI systems need constant updates to stay ahead of evolving fraud tactics and complex money laundering schemes. This means regularly improving models with new data and threat patterns and using strong operational practices like MLOps (Machine Learning Operations) and LLMOps (Large Language Model Operations). Embedding these frameworks into the AI lifecycle ensures fraud detection systems stay flexible, effective, and reliable over time.
Empowering Safer Transactions with Agentic AI Framework
Wipro’s Agentic AI framework, developed by Wipro Innovation Network (WIN), leverages the WEGA Responsible AI principles to enable real-time fraud detection with ethical and transparent decision-making. Its agentic intelligence dynamically adapts to evolving threats while ensuring compliance with global regulatory standards. The platform delivers instant alerts for suspicious activity, supports scalable enterprise deployment, and upholds trusted AI governance—empowering financial institutions to stay ahead of fraud and provide safer customer experiences.